Definition Of Rotation In Physics
Cool Definition Of Rotation In Physics 2022. In rotation, there is a central point that remains. In fact, all of the linear kinematics equations have rotational analogs, which are given in table 6.3.
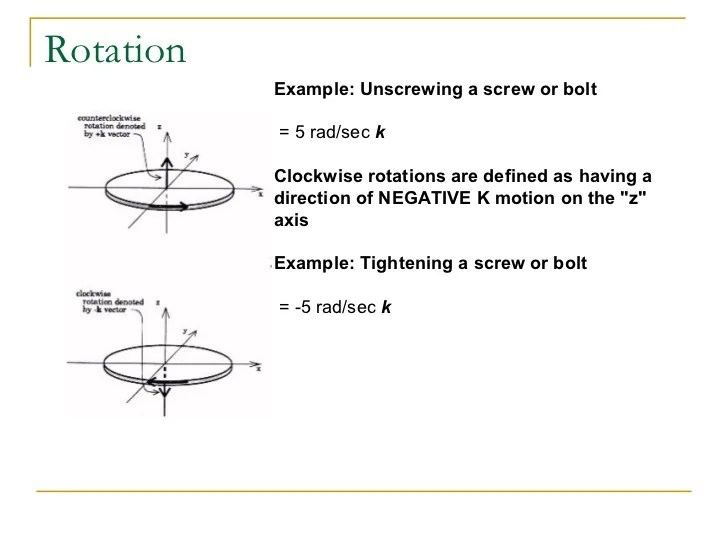
The cyclic oscillation of an item around a center is known as rotation. A full rotation is 360°. When two equal and opposite forces act parallelly on an object, the multiplication.
The Motion Associated With The Sliding Motion Of An Object Along One Or More Of The Three Dimensions, I.e., \ (X,\,Y\), And \ (Z\), Is Known As Translational.
Negative degrees of rotation move the figure in a clockwise direction. The rotation may be done. Rotational inertia is the proper physics term for why you spin faster on an office chair when your arms and legs are tucked in rather than spread out.
The Physics Behind Rotational Motion Is Described By A Concept Known As Kinematics.
Read a dialog where a student and a teacher work towards defining rotations as precisely as possible. Divide the circle into equal n parts by cutting an equal number of slices passing through the circle',s center. The angular displacement required to.
These Equations Can Be Used To Solve Rotational Or Linear Kinematics Problem In Which A And.
When two equal and opposite forces act parallelly on an object, the multiplication. Kinematics is a field within physics that focuses on the motion of an. Imagine going to the rest frame of a massive particle.
In This Frame, There Is Rotational Symmetry, Which Means That The Lie Algebra Of Rotations Acts On The Wave Function.
The dialog below is between a teacher and a student. Rotation has a central point that stays fixed and everything else moves around that point in a circle. The dynamics for rotational motion are completely analogous to linear or translational dynamics.
The Cyclic Oscillation Of An Item Around A Center Is Known As Rotation.
Angular displacement the angle swept out by the circular. In fact, all of the linear kinematics equations have rotational analogs, which are given in table 6.3. (r1) a rotation maps a line to a line, a ray to a ray, a segment to a segment, and an.
Post a Comment for "Definition Of Rotation In Physics"